From Digital Gold to Tokenized Worlds: A Modern Guide to Understanding Cryptocurrency

From Digital Gold to Tokenized Worlds: A Modern Guide to Understanding Cryptocurrency
In just over a decade, cryptocurrency has evolved from a niche curiosity for cryptographers into a multi-trillion dollar global asset class that is capturing the attention of individual investors, major corporations, and governments alike. Yet for many, the world of crypto remains shrouded in complexity and buzzwords. What exactly is cryptocurrency? Is it the future of money, a new type of speculative investment, or something else entirely?
The simplest definition is that a cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual token that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (like the U.S. Dollar or the Euro), most cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning they are not controlled by any single entity like a bank or government. This decentralization is made possible by a revolutionary technology called blockchain.
But to truly understand crypto in 2025, we must look beyond this basic definition. Cryptocurrency is not just about creating new forms of digital cash; it represents a fundamental shift in how we think about value, ownership, and trust. It is the foundational layer of Web3, a new, more decentralized internet, and it is the technology enabling the tokenization of everything from stocks and bonds to real estate and art.
This guide will demystify the world of digital assets. We will explore the core principles that make crypto work, break down the key technologies behind it, and provide a clear framework for understanding the different types of assets that exist in this rapidly expanding universe.
The Problem Crypto Solves: A New System of Trust
To grasp the importance of cryptocurrency, it's essential to first understand the problem it was designed to solve: the need for a trusted intermediary. In traditional finance, every transaction requires a central party—a bank, a credit card company, a government—to verify, record, and settle it. We trust these institutions to maintain the ledger and ensure that no one spends the same money twice.
This centralized model has worked for centuries, but it has limitations. It can be slow, expensive (think international transfer fees), and exclusive, leaving billions of people around the world without access to basic financial services. It also concentrates immense power and control within a few large institutions.
Cryptocurrency, starting with the invention of Bitcoin in 2009, proposed a radical solution. What if we could create a financial system that didn't rely on a central authority? What if we could build a system where trust is not placed in an institution, but is instead guaranteed by mathematics and a distributed network of computers? This is the core promise of blockchain technology.
How It Works: The Three Pillars of Cryptocurrency
At the heart of every cryptocurrency are three core concepts that work together to create a secure, decentralized system.
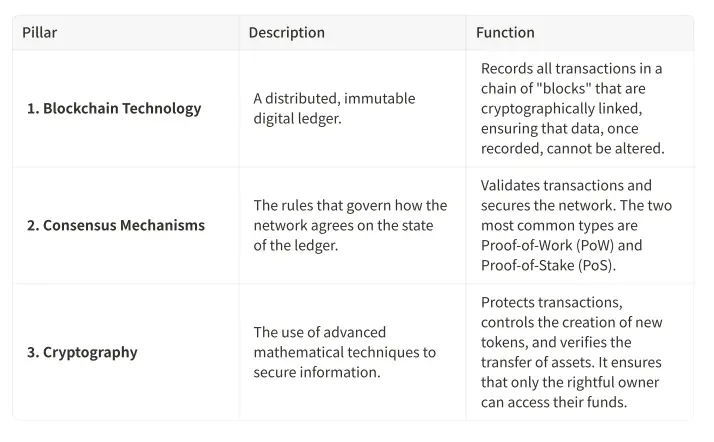
Pillar 1: The Blockchain - A Digital Book of Records
Imagine a shared digital notebook that is duplicated and spread across thousands of computers around the world. Every time a transaction occurs, it is recorded in this notebook. Before the new entry is added, the network of computers must collectively agree that it is valid. Once added, it is linked to the previous entry using a cryptographic signature, creating a chain of records. This is the essence of a blockchain. Its decentralized and linked nature makes it incredibly secure; to alter a single transaction, a hacker would need to simultaneously alter the same record on thousands of computers, an almost impossible feat.
Pillar 2: Consensus - How the Network Agrees
If there is no central authority, how does the network agree on which transactions are valid? This is achieved through a consensus mechanism. The original mechanism, used by Bitcoin, is Proof-of-Work (PoW). In this system, powerful computers known as "miners" compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first to solve the puzzle gets to add the next block of transactions to the chain and is rewarded with newly created cryptocurrency. This process is incredibly secure but consumes a significant amount of energy.
A more modern and energy-efficient alternative is Proof-of-Stake (PoS). In a PoS system, participants known as "validators" lock up or "stake" their own cryptocurrency as collateral. The network then randomly selects a validator to create the next block, with the probability of being chosen often proportional to the amount staked. If a validator tries to add a fraudulent transaction, they risk losing their staked funds, creating a powerful economic incentive to act honestly.
Pillar 3: Cryptography - Securing Your Digital Assets
Cryptography is what puts the "crypto" in cryptocurrency. When you own a digital asset, what you really own is a private key. This is a long, complex password that gives you the ability to authorize transactions from your account. This private key is linked to a public key, which is a publicly visible address that others can use to send you funds. This system, known as public-key cryptography, ensures that only you can access and control your digital assets.
Beyond Bitcoin: The Expanding Universe of Digital Assets
While Bitcoin introduced the world to cryptocurrency, the industry has since exploded into a diverse ecosystem of different types of digital assets, each with its own unique purpose and value proposition.

Is Cryptocurrency a Good Investment?
Investing in cryptocurrency can be highly rewarding, but it also comes with significant risks. The market is known for its volatility, with prices capable of swinging dramatically in short periods. However, the long-term trend has shown remarkable growth, and the increasing adoption of digital assets by institutional investors and major corporations suggests that the asset class is maturing.
A modern approach to crypto investing involves looking beyond simple price speculation and focusing on the underlying utility and long-term potential of different assets. A well-diversified portfolio might include:
A core holding of established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
An allocation to stablecoins for stability and liquidity.
Exposure to promising smart contract platforms and DeFi protocols
An investment in tokenized real-world assets to blend the benefits of blockchain with the stability of traditional investments.
Platforms like Slaff.io are at the forefront of this new paradigm, offering a multi-asset platform where users can manage their traditional finances alongside a diversified portfolio of digital assets, including cryptocurrencies and tokenized funds.
The Future is Regulated: MiCA and the Path to Mainstream Adoption
For years, the lack of regulatory clarity was a major barrier to mainstream adoption. That is now changing. Landmark regulations like the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) framework in the European Union are providing a clear rulebook for the industry. These regulations are designed to protect investors, prevent financial crime, and ensure the stability of the market, all while fostering innovation.
This new era of regulation is a sign of the industry's maturation. It provides the certainty that institutional investors and large corporations need to enter the space, and it gives everyday users the confidence that they are operating in a safe and transparent environment. Far from stifling the industry, a clear and sensible regulatory framework is the final piece of the puzzle that will unlock the full potential of digital assets.
Conclusion: A New Financial Operating System
Cryptocurrency is more than just a new asset class; it is the foundation of a new financial operating system. It is a technology that enables verifiable digital ownership, decentralized trust, and the seamless transfer of value across the globe. From its origins as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, it has blossomed into a sprawling ecosystem that is tokenizing the world, rebuilding the infrastructure of finance, and creating a more open and accessible global economy.
Understanding cryptocurrency is no longer just for tech enthusiasts or speculative traders. It is becoming an essential part of financial literacy in the 21st century. As the lines between the traditional and digital financial worlds continue to blur, those who grasp the fundamental principles of this transformative technology will be best positioned to navigate the future of finance.



